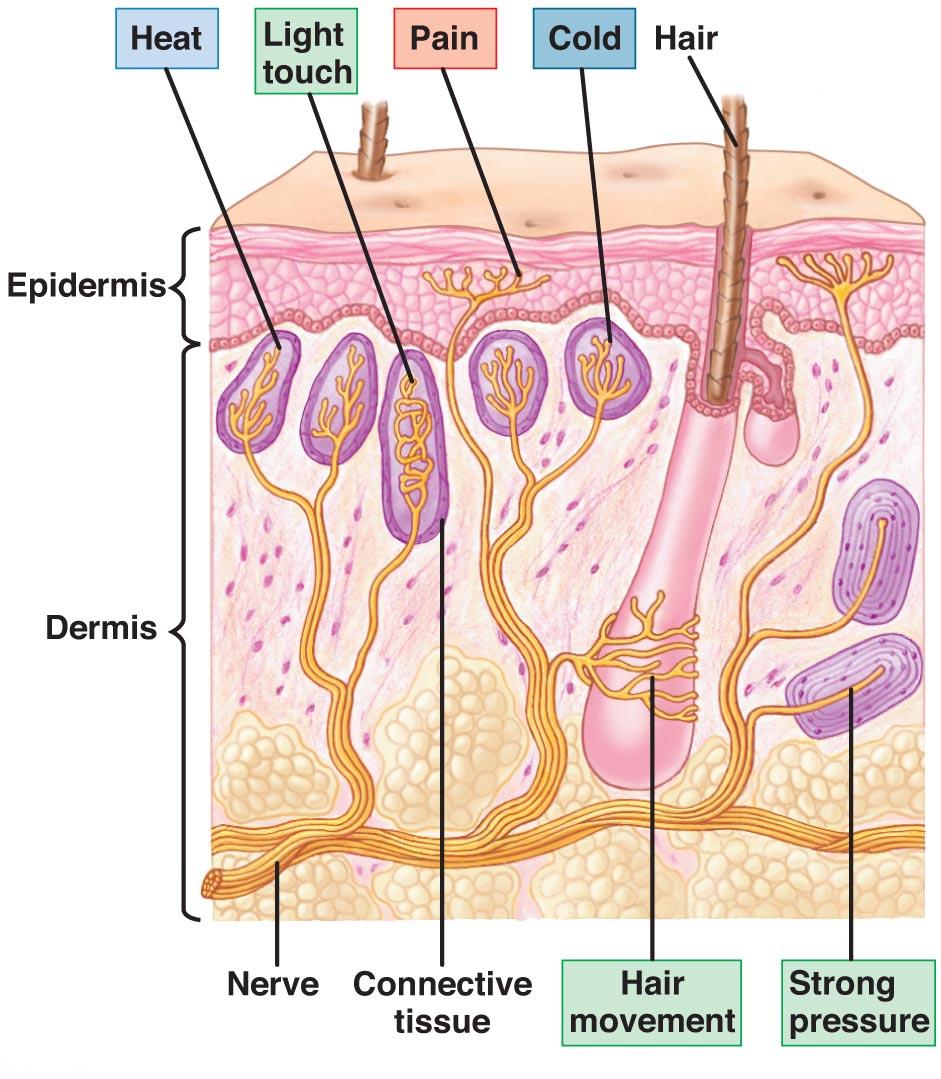
Pacinian corpuscles are said to be the pressure receptors (Loewenstein, 1961). They are found in the deeper layers of the skin, in the connective tissue around the tendons, muscles and joint and in the serous membranes and mesenteries of the viscera.
They are very large in size, reaching almost 1 mm in length and 0 .6 mm in diameter. These are primary sense cells in which the terminal portion of the nerve fibre that is nerve end which is non-‘myelinated, is surrounded by a relatively thin granular mass- and covered by concentric layers of connective tissue like the many coats of an onion.
The concentric layers or laminae are separated by fluid which helps in transmitting the superficial pressure changes to the delicate nerve ending within.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The concentric layers or laminae constitute the auxiliary apparatus and do not take part in the generation of electric potentials.
When the nerve endings of these receptors, either inside or outside, are subjected to increased pressure, the membrane potential in the region of the nerve endings is decreased with the result action potential in the form of nerve impulse is developed which is according to local circuit theory is transmitted down to the axon and ultimately reaches the central nervous system which acts accordingly.
Pain is a sensory experience initiated by injurious or threatening stimuli. There are both painful sensations and reflex actions in response to painful stimuli.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Intensive stimulation of almost any sensory neuron appears capable of producing a painful sensation and only recently has it been shown that specialized receptors for pain exist.
Generally the sensation of pain is evoked by either of two sets of nerve fibres. Some fibres when sufficiently stimulated result in burning pain ; small fibres function in signalling pricking pain.
The latter is usually a short term effect, while the former may continue for long periods of time as long as the stimulus remains.
Touch receptors of various kinds are located in the dermis or in the subepidermal connective tissue, they have a basic structure of nerve endings or tactile cells enclosed in layers of connective tissue.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Tactile receptors are found all over the skin in the animals and include wide variety of morphological types.
Many have the forms of bulbs (Krause end bulbs) or corpuscles (Meissner’s corpuscles). Meissner’s corpuscles are generally found in the outer layer of the skin.
Touch receptors not only convey information a out the presence of tactile stimuli but they also possess discriminatory abilities for both the intensity of the stimulus and for the spatial direction or arrangement of the stimulus.
The greatest ability to discriminate between intensities of stimulation or to determine the extent of spatial separation of separate stimuli occurs in areas of greatest concentration of sensory receptors.