Energy is the ability to do work. Broadly, there are six types of energies, viz. Mechanical, Radiant, Chemical, Heat, Electrical and Nuclear. Mr. CHEN is a mnemonic for remembering the six forms of energy.
Types of Energy
The different types of energies are briefly described below:
(i) Mechanical Energy:
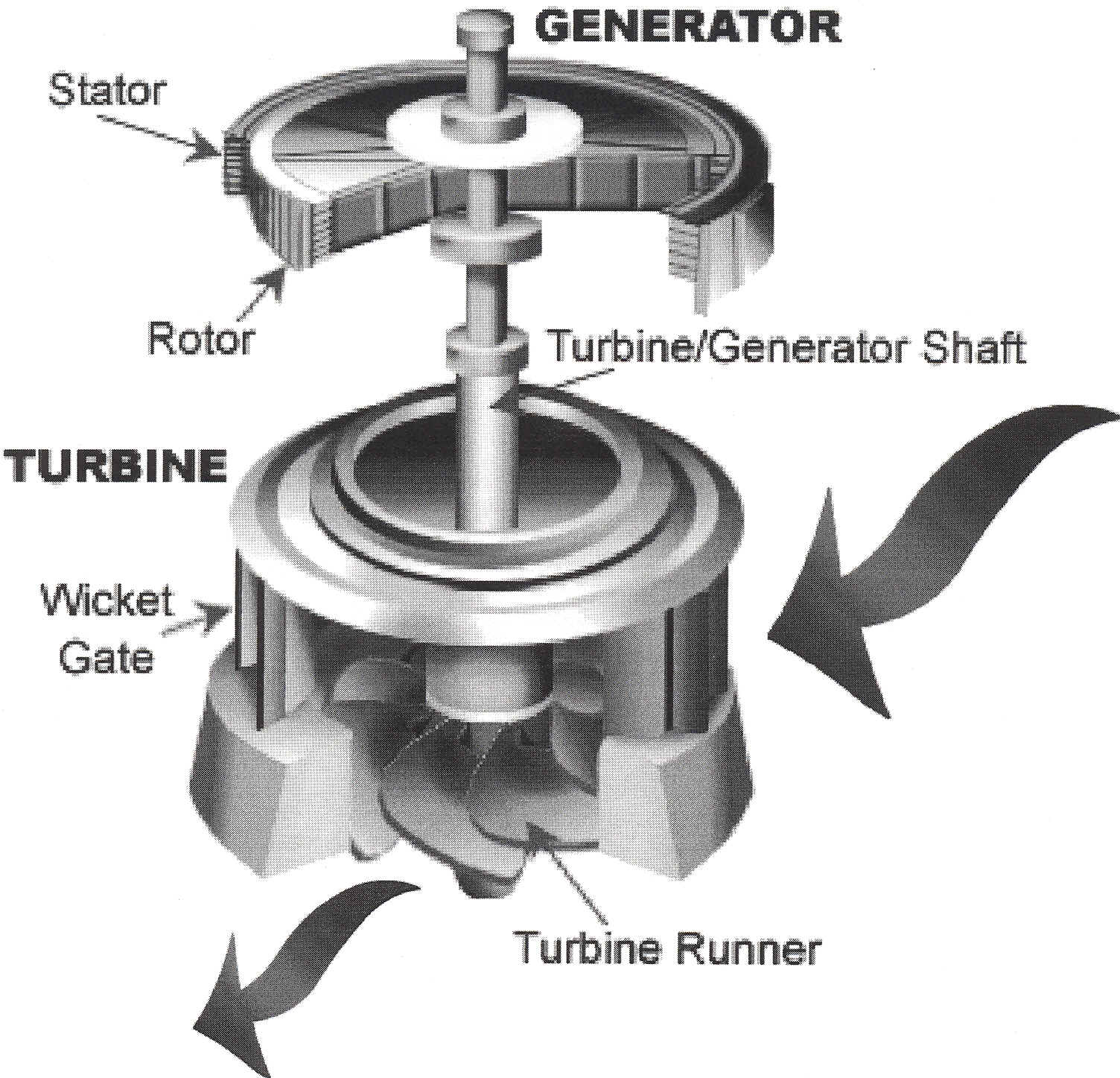
Energy due to object’s motion (kinetic) or position (potential) is known as mechanical energy. Examples: Windmill used to make electricity, water wheel used to grind grain.
(ii) Radiant Energy:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Radiant energy is electromagnetic energy. It includes energy from gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light, infrared rays, microwaves and radio waves. Examples: Solar panel used to provide electricity and heat for a house; microwave oven used for cooking.
(iii) Chemical Energy:
Energy that is available for release from chemical reactions is termed as chemical energy. Example: Gasoline is used to run a car.
(iv) Heat Energy:
The heat energy of an object determines how active its atoms are. Example: Coal is used to produce steam for a steam engine of train.
(v) Electrical Energy:
Energy caused by the movement of electrons is called electrical energy. Example: Electricity is used to run appliances in our home.
(vi) Nuclear Energy:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Nuclear energy is the energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. It is the energy that holds the nucleus together. It is released when the nuclei are combined (Nuclear Fusion) or split apart (Nuclear Fission).
Example:
Nuclear power plant uses the fission of atoms to create energy that is converted into electricity.
According to the First Law of Thermodynamics, “Energy is never created nor destroyed, but it can be converted from one type into another.”