Product Selection and Development Process are very complex process, which begins with idea generation and continues till commercialization. The process requires coordination between various departments. The process can be broken up into the following stages:
1. Exploration:
New ideas are sought from the sales force, since that is the department which is in constant direct contact with customers.
The analysis of customer needs also takes into account competitors’ products and services. New ideas are also generated from the consultants, shareholders, management employees, report on foreign markets and products, trade journals, R&D laboratories, other research, etc. However, technical feasibilities and market potential have to be kept in mind while examining new ideas.
2. Screening:
ADVERTISEMENTS:
While choosing the most effective ideas, guesswork or hunches are not reliable. To ensure a more scientific and less risky selection process, it is necessary to keep in mind all possible quantitative, as well as, qualitative information. Keeping in mind the organizational objectives and available facilities, the following must points be considered while selecting an idea—
i. Market potentiality
ii. Technical feasibility of the idea
ADVERTISEMENTS:
iii. Does the idea fall under any intellectual property rights or patent regulations?
iv. Raw material supply position—at present and in the future
v. Do existing production facilities and resource availability remain suitable for commercialization of the new idea?
vi. The level of investment required
ADVERTISEMENTS:
vii. Can the company generate this level of required investment from internal sources?
viii. If borrowing is a must, cost of borrowing is a factor
ix. Does profitability projection analysis suggest adequate return on investment?
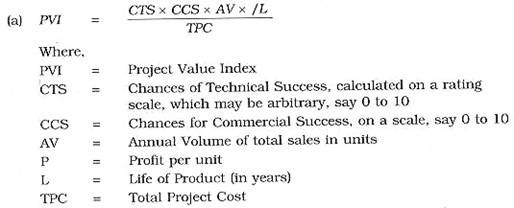
Profitability projection study can be made using following formulae:
However, a more simple approach, as under, may be considered to arrive at the net probable return per rupee:
In addition, point system and graphs also can supplement the profitability projection analysis of new product.
3. Business Analysis:
At this stage, technical and economic factors, like manhours, cash flow, inventory holding, etc., are analysed to evaluate commercial feasibility. This will ultimately facilitate the budgeting process.
4. Development:
A working model is developed at this stage to evaluate the practicability of the new idea, by studying the acceptability of customers to the working model. Most companies use product life cycle model at this stage.
5. Testing:
Redesigning of the working model into a production prototype and testing the market before bulk production.
6. Commercialization:
At the final stage of a new product planning, decisions have to be made whether to make or buy components; production methods have to be developed; distribution networks activated and the new product has to integrate with the organization’s normal activity, and satisfactory sales volume and profitability have to be achieved.